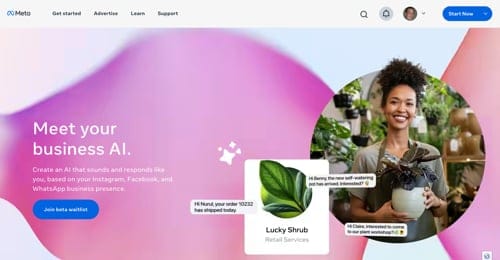
As retailers continue to explore how artificial intelligence (AI) can improve their business, agentic AI represents a seismic shift. Agentic AI is autonomous intelligence that can learn and act independently.
Think of agentic AI as a digital employee that doesn’t have to wait for instructions. It learns, adapts, and acts on its own, presenting an opportunity for retailers to enhance customer experiences (CX) and add value in new ways.
Unlike traditional AI tools, which execute programmed responses based on predefined rules and a limited knowledge base, agentic AI systems take actions independently and proactively.
For example, agentic AI can continuously analyze individual customer behavior patterns to enable real-time decisions, such as offering a customized discount to a customer who has abandoned their shopping cart. Its ability to operate without human prompting allows the AI to determine the best marketing approach for each customer and then make changes to that strategy based on the customer’s actions.
This process can help retailers move away from a one-size-fits-many approach to marketing and bolster an agile, hyper-individualized customer journey that evolves with each interaction, such as dwell time or customer clicks.
Many retailers are already investing in AI and have been for some time. Thanks to their relative AI maturity, and because the upfront investment required to adopt agentic AI has become smaller, retailers of all sizes may find it to be more accessible to them than other industries.
But even though agentic AI is growing in popularity, retailers must prove its business case to stakeholders while also putting robust risk management protocols in place.
From Simple Chatbots to Intelligent Shopping Companions
Table of Contents
Past chatbots and virtual assistants had a limited knowledge base with which to answer customer questions. If the AI was not trained in a certain way or did not have data to answer specific inquiries, customers often hit a dead end. For example, if a customer asks to see a specific piece of inventory, an AI assistant could help but could not handle more complex customer support needs.
With generative AI taking off recently, customers can now make highly specific requests. For instance, a customer could ask a digital assistant to recommend light-yellow shirts that are appropriate for a wedding welcome party in the summer months. Generative AI can not only recommend options but offer to put together an entire outfit. However, agentic AI can take the customer experience even further.
Agentic AI incorporates generative AI to still provide the same recommendations tailored to individual customer profiles but can act like more of a digital assistant. With agentic AI, the digital assistant can check product availability in the customer’s preferred sizes, apply available loyalty discounts or promo codes, or reserve the items for in-store pickup.
Agentic AI’s capabilities move users from suggestion to action and can handle the transactional steps that generative AI alone cannot perform, thereby enhancing CX. Because it leverages connected databases and advanced AI modeling, agentic AI can better support complex, omnichannel customer journeys.
But taking over shopping logistics is just one of many potential applications. By combining customer behavior data with macro factors like seasonality, real-time inventory levels, and upcoming product deliveries, agentic AI can also autonomously calculate bespoke pricing in real time.
For instance, a shopper on a retail website powered by agentic AI could see a tailored price or discount for an item based on their browsing habits, budget, and promotions the retailer is willing to offer. With agentic AI running the process, retailers can repeat this approach across thousands of customers to increase conversions and sell through. Implementing dynamic pricing at scale allows each consumer to feel like they have a personal shopping assistant that knows their preferences and price range.
For retailers further along in their digital transformation and AI journeys, agentic AI is a natural next step. It can provide cost efficiencies and marketing benefits that greatly improve CX. To get started, retailers should pick a use case that is simple and has demonstrable return on investment.
How to ID a use case that is right for you:
|
Educate Employees & Identify a Task: It is important to pick a task that agentic AI can manage easily, allowing it to make decisions autonomously with the information to which it has access. At the same time, retailers should explain how using AI for this task or goal will benefit employees. It’s crucial to help employees understand the value that AI can bring them. |
|
|
Define Your AI Strategy: Once your use case is identified, consider how it will provide immediate, measurable value to the company for the least amount of risk. Then, benchmark what success looks like for the chosen use case and outline expected and quantifiable ROI. |
|
|
Establish the Foundation: AI relies on strong data that is structured, accurate, and clean. Once the foundation is set, consolidate customer data from all touchpoints to create comprehensive behavioral profiles that fuel agentic AI decision-making. |
|
|
Prepare Your People: Make sure that the teams directly impacted by the project understand how it will change their daily workflow. Adjusting the workflow will be necessary to enhance automation where possible, while still ensuring human oversight is in place throughout the process. |
|
|
Go and Grow: Experiment with agentic AI as new use cases emerge to increase effectiveness. Assess the performance of the first use case, communicate success, and empower teams to think creatively about how AI could help them in their work. Iterating on use cases and showcasing efficiencies is critical for capturing stakeholder buy-in. |
Building the Business Case: ROI and Risk Management
To prove the ROI of agentic AI and achieve stakeholder buy-in, retail executives should:
- Define Clear Objectives: Retail leaders should outline their main goals in leveraging agentic AI. Are they hoping to achieve rapid customer acquisition, grow lifetime value, or improve conversion rates for existing traffic? Is there another business benefit they want to pursue?
- Develop the Solution Design: For agentic AI to be successful, retailers must build an architecture that enables access to real-time data streams and integrates with existing systems. Thinking through technology infrastructure and connectivity before piloting AI can help prevent time and resource misuse.
- Deploy an Integrated Data Approach: Aim to combine customer behavior data, macro factors such as seasonality and economic fluctuations, as well as real-time inventory intel to deliver individualized experiences that map to key moments in the buyer’s journey.
- Measure Impact and Key Performance Indicators (KPI): There are different ways to measure the results of agentic AI investments. Retailers should outline upfront what these metrics are and why they matter. For example:
- Financial returns are an important KPI. Retailers may look for increased conversion rates, higher-average order values, or improved inventory turnover via precision targeting.
- Operational efficiency is another way to measure success and can take numerous forms. Metrics may include increased employee productivity, reduction (or elimination of) data silos from well-integrated systems, or improved accuracy in customer insights that drive better business decisions.
As retailers make their business case and prepare their organization for agentic AI adoption, retailers must also consider the key risks associated with agentic AI. Mapping out the risks, and understanding how to mitigate them, is an essential step on the road to launching agentic bots.
Retailers should also prioritize cybersecurity. Because the integrated systems that power AI require access to multiple data sources, AI adoption can increase the attack-vector surface and create new entry points for potential security breaches. A well-crafted cybersecurity program can help reduce this risk.
Beyond external-facing cybersecurity concerns, autonomous AI can introduce new risks via its day-to-day functions. Deploying agentic AI can increase the risk that shoppers will cause it to inadvertently leak sensitive information due to its ability to reason and answer independently. A customer could ask for information that falls outside of the scope of an agentic AI’s remit, an act known as “prompt injection.”
For example, a customer might be having a conversation with a bot about garment pricing and then ask the AI to reveal information about the company’s finances and revenue generation. Without the proper protocols in place, agentic AI might divulge this intel. It’s critical for retailers to filter to avoid prompt injection, and certain models should be restricted to prevent agents from answering questions that reveal critical business data.
Effective risk mitigation also requires pilot testing agentic AI in a controlled environment. Testing allows retail executives to validate autonomous decision-making and refine algorithms before full-scale deployment, thereby reducing risk.
A fashion retailer might pilot agentic AI by creating a closed sandbox environment using historical data from a specific product category, like women’s dresses from the previous season. In this controlled environment, the AI model could practice making autonomous pricing decisions based on simulated customer behavior patterns, inventory levels, and trends, but without the risk of those decisions affecting live customer experiences or actual pricing.
Reimagining the Retail Experience
Agentic AI is poised to reshape retail marketing. By enhancing personalization and enabling precise customer targeting, it can offer a future-forward shopping model that is highly individualized, independent, and repeatable at scale. With these efficiencies and the deepened customer loyalty they can bring, retail executives can drive long-term growth during a critical industry inflection point.