Google’s Web Guide is an experiment launched in July 2025 that uses AI to organize a user’s search results. To try the feature, enable it in Google Labs.
Unlike a fan-out (which guesses what additional information is helpful in a searcher), Web Guide analyzes the content of top-ranking pages and groups them by topic.
AI then summarizes each category, providing an overview of the pages.
Perhaps unintentionally, Web Guide is handy for search engine optimization by revealing Google’s understanding of keywords.
Targeted queries
Organic search results order web pages by ranking signals. Yet searchers cannot easily discern the pages’ content type or topics without visiting each one. Web Guide provides a summary, thus implying how Google interprets a query.
For example, Web Guide groups the search results for “how to build a website” by the following topics:
- “Comprehensive guides to building a website”
- “Building websites with no-code builders”
- “Creating websites with Google Sites”
- “Website building with Squarespace”
- “Building websites with Wix”
- “Building websites with Canva”
- “Website development with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript”
- “Learning web development: courses & tutorials”
- “Choosing website builders”
- “Community advice on website building (Reddit threads and forums)”
- “Understanding domain names and hosting”
- “Web design principles and best practices”
Creators looking to search-optimize an article or course on website building can use the list for topics to include.
Web Guide can also identify competitors. For example, searching “waterproof sneakers” in Web Guide generates a section of the best-known brands:
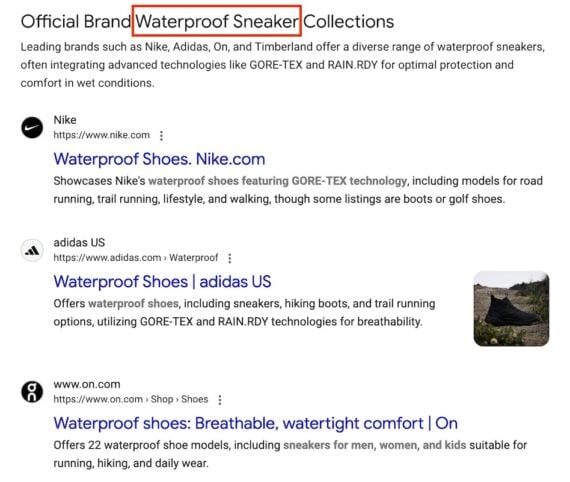
Web Guide can identify competitors, as shown in this example for “waterproof sneakers.”
It also reveals alternative keywords to target, such as “water resistant” and “water shoes”:
Water-Resistant and Water Shoes
Some sneakers offer water resistance or are designed as full water shoes, with specific technologies like HDry® membrane providing complete waterproofing and breathability, while others prioritize quick drying.
Brand search
Searching for a brand name in Web Guide provides insight into what Google knows about the company and the URLs that impact its understanding. For example, searching “home chef” in Web Guide generates a separate section for the prices of that service. AI summarizes each ranking page.
Web Guide results also help brands ensure off-site consistency and identify which user-generated content to monitor. For example, brands that change pricing can use Web Guide to find a list of URLs to update.
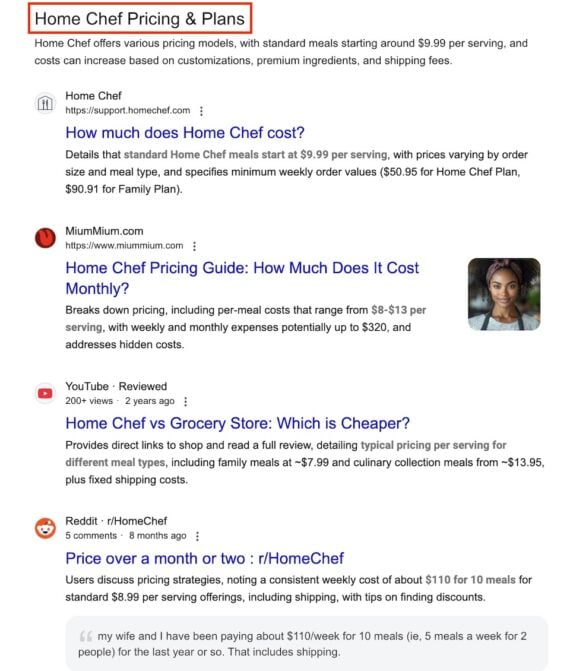
Searching for “home chef” in Web Guide returns a section on pages that address the service’s prices.
Competitors
Queries in Web Guide reveal its preference among competitors. Take “Home Chef” and “Green Chef,” for example. Searching “home chef vs green chef” reveals Web Guide’s AI prefers the latter:
Green Chef typically comes out ahead due to its organic ingredients, health-conscious dietary plans, and sustainability efforts, whereas Home Chef offers greater affordability, customization, and convenience with quick-prep meals.
The URLs listed below the initial summary are also AI-summarized, offering a list of publications and authors to contact for clarifications or enhancements.
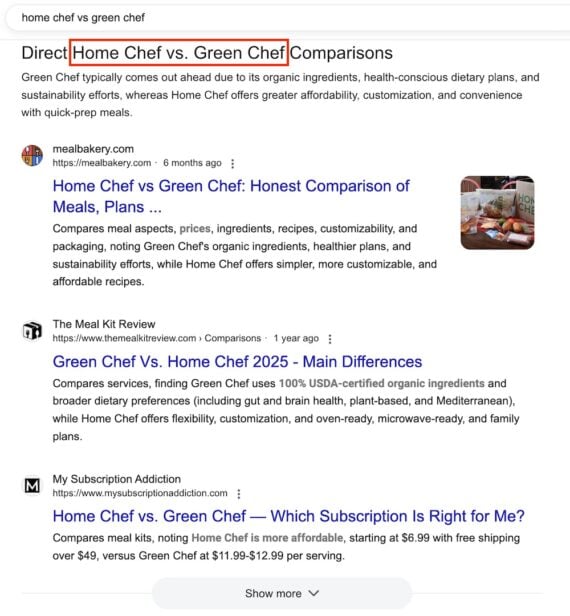
Queries in Web Guide reveal Google’s preference for top competitors, such as this comparison of “Home Chef” and “Green Chef.”
Web Guide may or may not become public. Many such Google Labs experiments never do. While aimed at consumers, it implicitly helps search optimizers by revealing how Google’s AI interprets a query or understands a brand.